Plasmolysis Definition Biology
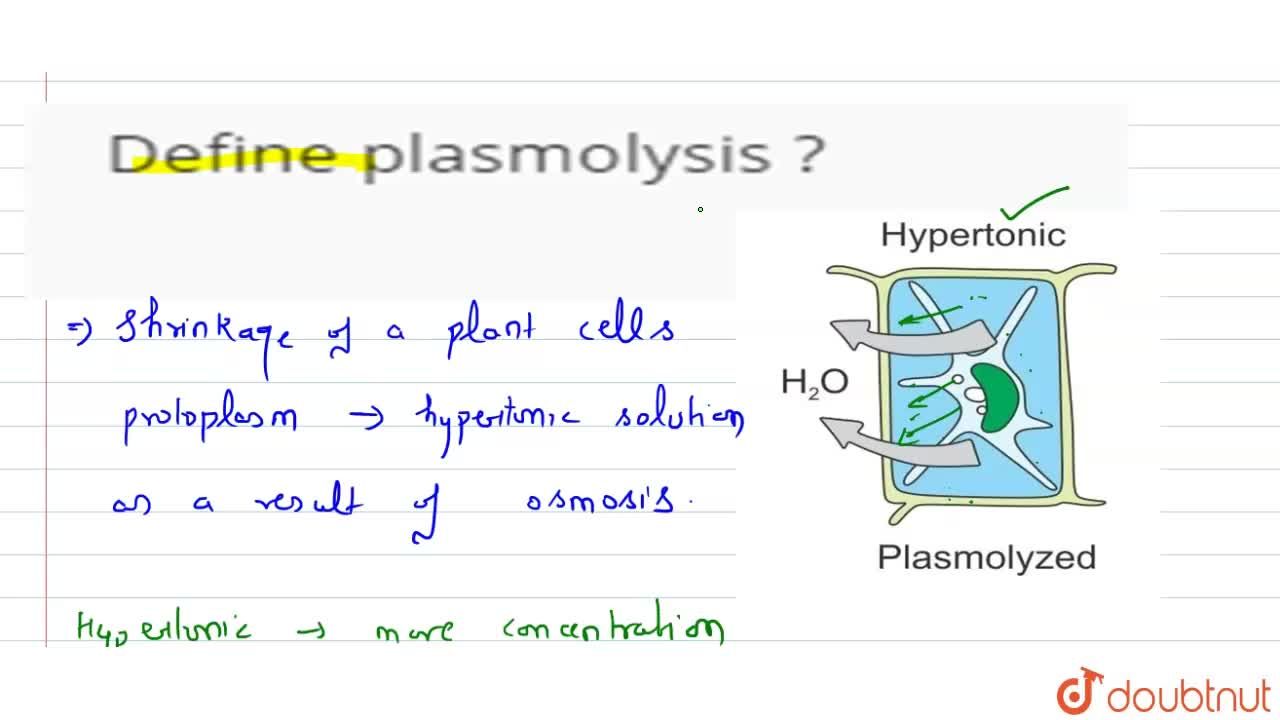
Plasmolysis definition biology. In summary plasmolysis is the process of water flowing out of cells causing them to shrink. Plasmolysis is derived from the Greek and Latin word ie plasma which means the mould and lysis which means loosening. Definition Movement of water Process Effect on plant cell.
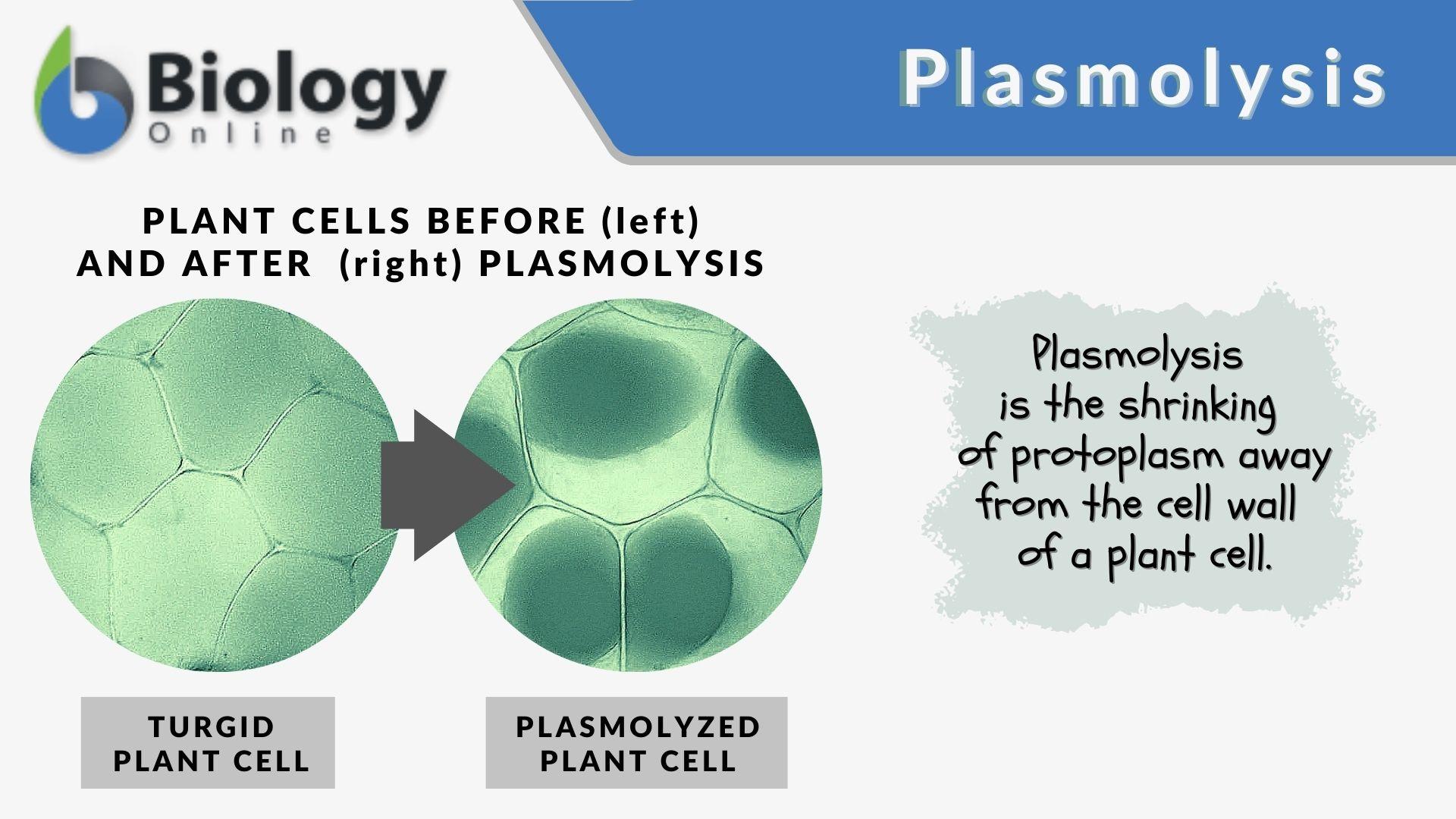
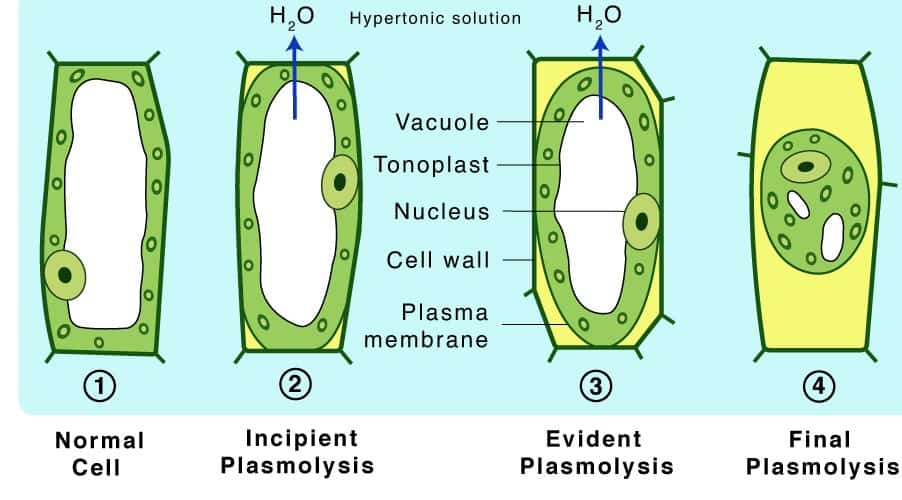
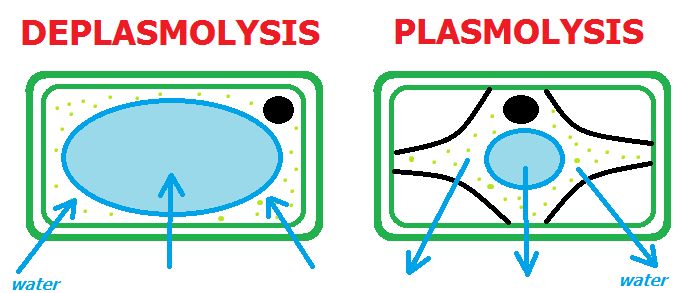
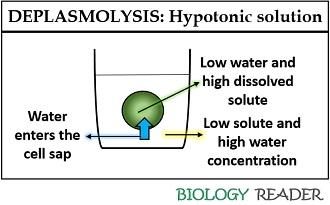
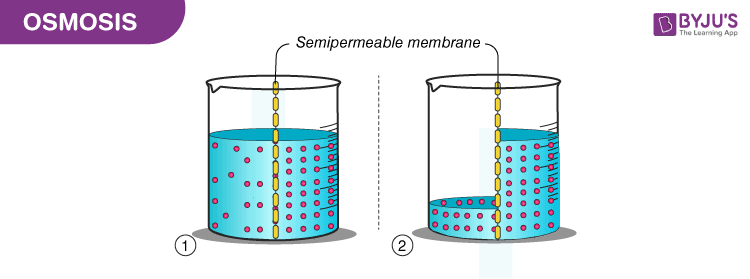
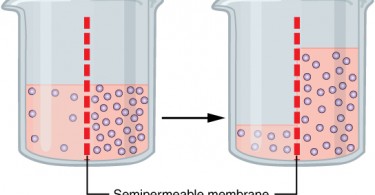
Plasmolysis is the process whereby the protoplasm of a plant cell shrinks away from its cell wall. Plasmolysis is a cellular state of plant cells in which after a loss of water the membrane pulls away from the cellulose-pectin wall. The reverse process deplasmolysis or cytolysis can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a lower external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell.
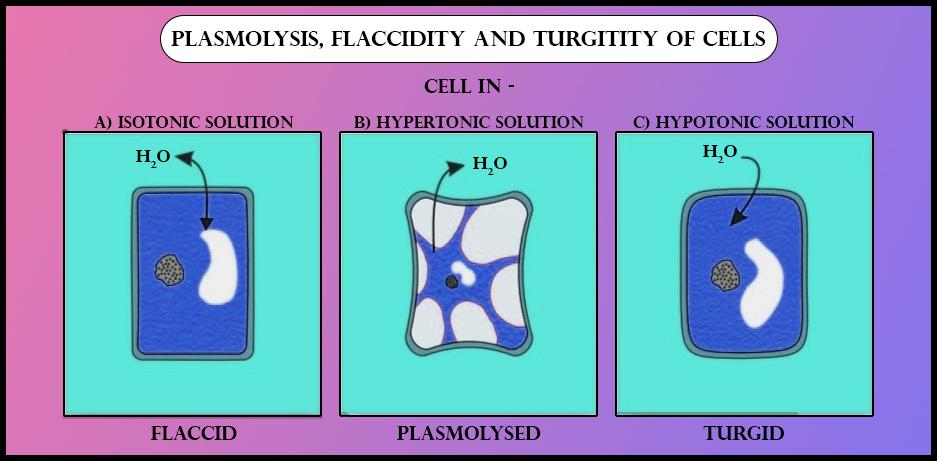
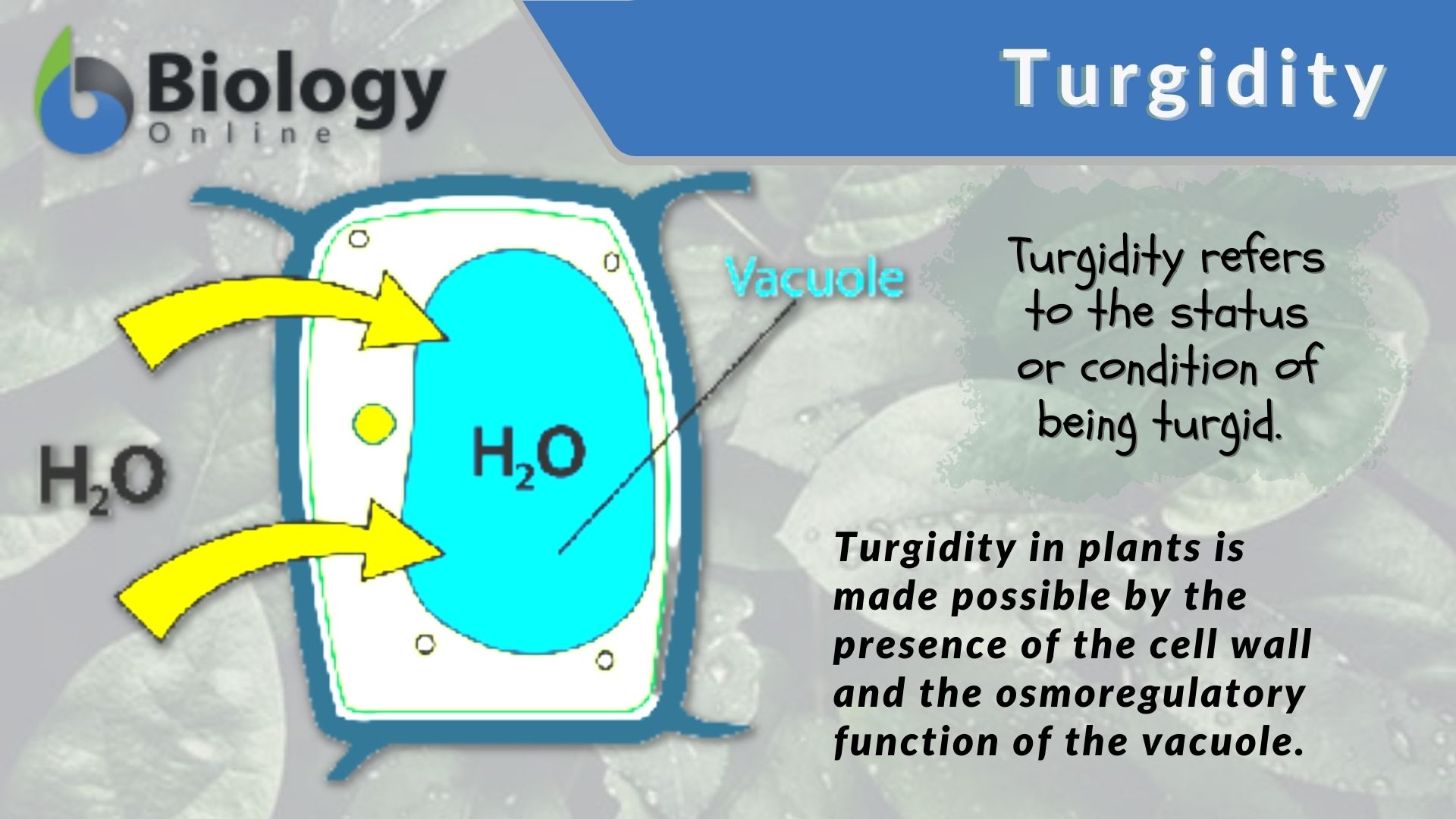
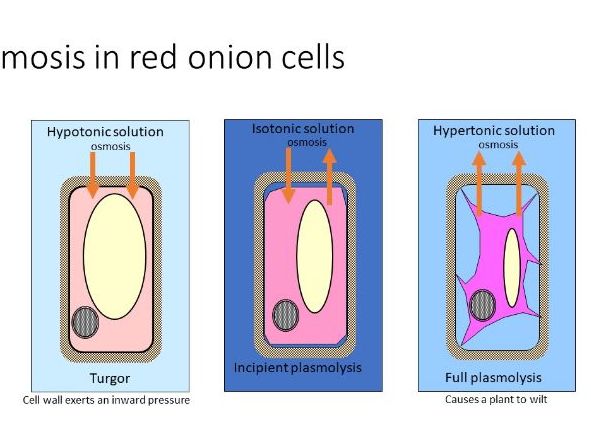
Hypertonic environment or hotdry weather conditions may cause the cells with a cell wall to lose water. The plasmolytic process is mainly driven by the vacuole. It is the opposite to the state of turgidity.
Plasmolysis is an example of the results of osmosis and rarely occurs in nature. Plasmolysis occurs due to water molecules diffusing to their concentration gradient causing plants to lose water. Definition of Plasmolysis Plasmolysis can define as the exosmosis process which results in a net movement of water into the surrounding from the cell protoplasm when put in a hypertonic solution.
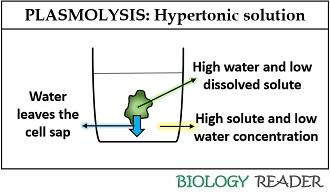
Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. C The Alterations in Surface Structure Caused by Osmotic Shock. Hypertonic solution causes exosmosis or withdrawal of water from cytoplasm and then the central vacuole of cell.
The word Plasmolysis was generally derived from a Latin and Greek word plasma The mould and lusis meaning loosening. Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water when placed in a hypertonic solution. The plasmolytic process is mainly driven by the vacuole.
Plasmolysis occurs when a flow of water leaves the plant cell and vacuole by osmosis. Types Of Plasmolysis Mild Plasmolysis.
The word Plasmolysis was generally derived from a Latin and Greek word plasma The mould and lusis meaning loosening.
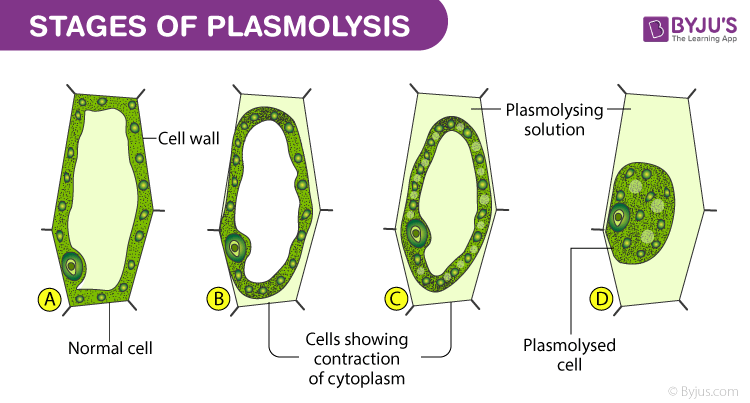
The reverse process deplasmolysis or cytolysis can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a lower external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell. Hypertonic environment or hotdry weather conditions may cause the cells with a cell wall to lose water. In summary plasmolysis is the process of water flowing out of cells causing them to shrink. Stay tuned with BYJUS to learn more about the plasmolysis stages and types of plasmolysis significance and other related topics at BYJUS Biology. Plasmolysis occurs when a flow of water leaves the plant cell and vacuole by osmosis. However in animal cells the net efflux of water causes the cells to wrinkle but the existence of the cell wall in plant cells. Plasmolysis may be defined as the shrinkage of all the protoplasm away from its cellulose wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. The vacuoles and the cytoplasm collapse or shrink away from the cell wall this state is called Plasmolysis. Plasmolysis is defined as the process of contraction or shrinkage of the protoplasm of a plant cell and is caused due to the loss of water in the cell.
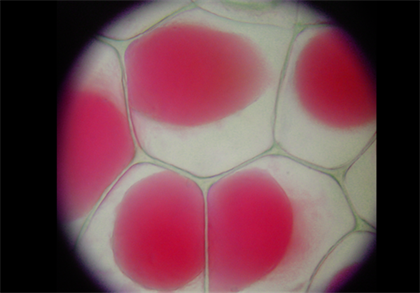
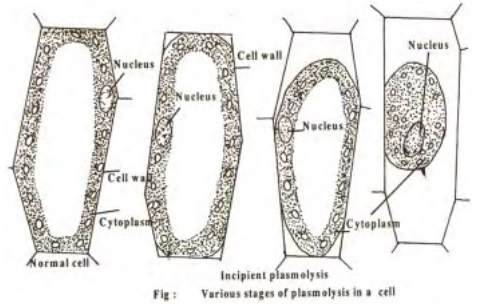
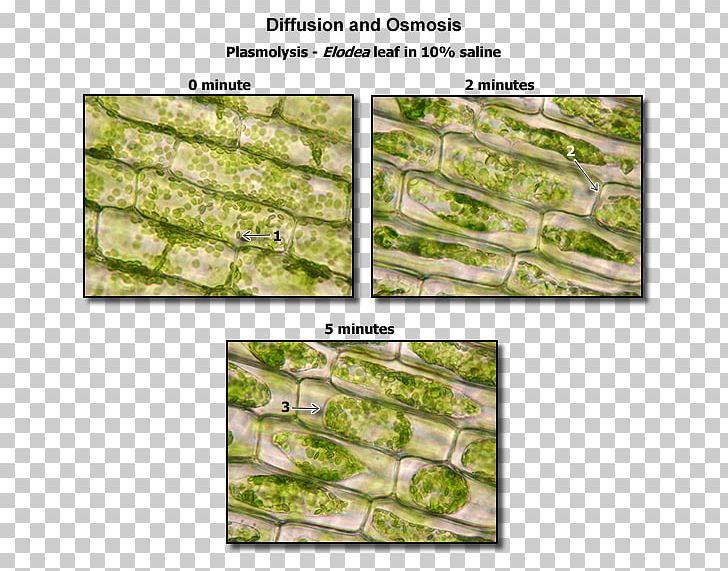
Plasmolysis can be shown in the laboratory by taking a living cell and placing it in a concentrated salt solution. Plasmolysis can be shown in the laboratory by taking a living cell and placing it in a concentrated salt solution. Noun shrinking of the cytoplasm away from the wall of a living cell due to outward osmotic flow of water. Plasmolysis is reversible deplasmolysis and characteristic to living plant cells. Plasmolysis may be defined as the shrinkage of all the protoplasm away from its cellulose wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. Plasmolysis is a typical response of plant cells exposed to hyperosmotic stress.


























.PNG)


Post a Comment for "Plasmolysis Definition Biology"